 Facepalm cat is embarrassed at people's ineptitude to correctly spell could have, should have, and would have.
Facepalm cat is embarrassed at people's ineptitude to correctly spell could have, should have, and would have. These are called past modal verbs, often referred to as the unreal conditional. We use these when talking about unreal events in the past - used to describe what someone should have done, could have done, or would have done, but didn't. Alternatively, it can be used to describe what someone shouldn't have done, couldn't have done, or wouldn't have done, but did.
The structure is as follows:
Could have + past participle
Should have + past participle
Would have + past participle
Couldn't have + past participle
Shouldn't have + past participle
Wouldn't have + past participle
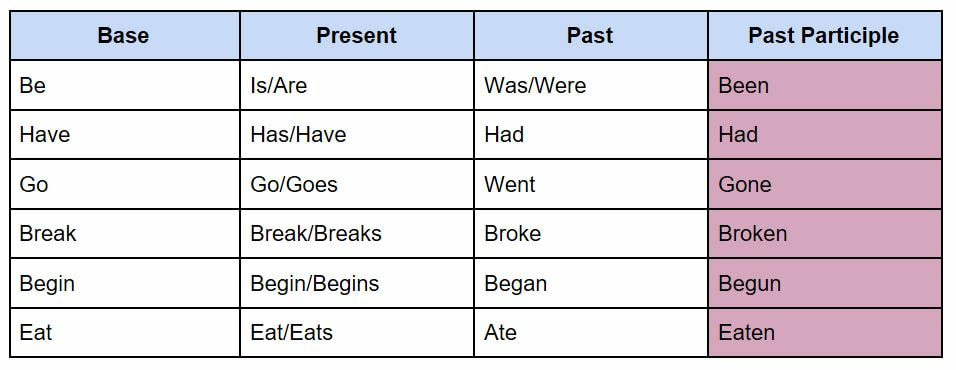
Examples of the past participle (irregular verbs):

I could have been an astronaut, but decided I wanted to be an English teacher.
He shouldn't have had that extra piece of chicken. He did, and now he feels sick.
We should have gone to Florida this winter, but decided to spend our money on concerts instead.
I could have easily broken my back shovelling. Good thing I have a snow blower!
If I were her, I would have begun the meeting by introducing all the participants. Now everyone is guessing who everyone else is.
I could have eaten more cake, but that would have been selfish.
Before I finish, I need to impart some invaluable knowledge. When speaking, it's OK to use the contracted form of these words. However, in formal writing, contractions are frowned upon, so correct spelling is incredibly important. To do otherwise reflects poorly on you.
So here is the official edict:
Could've = could have NOT could of
Should've = should have NOT should of
Would've = would have NOT would of
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed